Rac1: A Key Player In Cell Polarity And Migration, a protein best known for its role in regulating cell migration and polarity.
Editor's Notes: Rac1: A Key Player In Cell Polarity And Migration have published on today date. Rac1 is a small GTPase that is involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. It is also known to play a role in the development of cancer. Understanding the role of Rac1 in cell polarity and migration could lead to new treatments for cancer and other diseases.
Our team of experts has analyzed and digested the latest information about Rac1: A Key Player In Cell Polarity And Migration. Here is the guide that we have compiled to assist you in making an informed decision.
| Key Differences | Rac1: A Key Player In Cell Polarity And Migration |
|---|---|
| Definition | Rac1 is a small GTPase protein that is involved in a variety of cellular processes. |
| Function | Rac1 is best known for its role in regulating cell migration and polarity. |
| Importance | Understanding the role of Rac1 could lead to new treatments for cancer and other diseases. |
Main Article Topics
FAQs
This page addresses frequently asked questions about Rac1, an essential player in cell polarity and migration.Rac1: A Key Player In Cell Polarity And Migration
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Rac1: A Regulator of Cell Migration and a - Source www.mdpi.com
Question 1: What is Rac1?
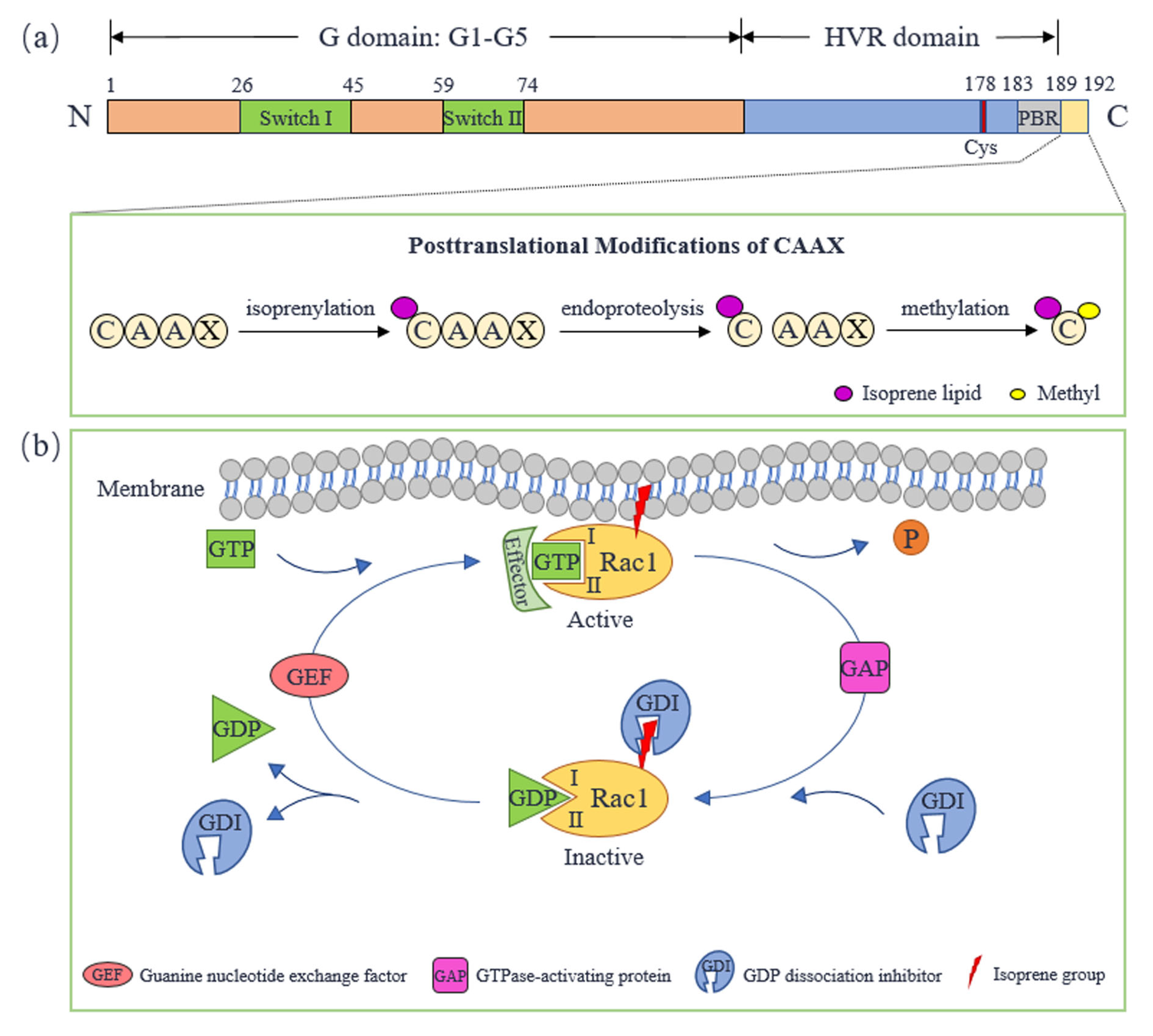
Rac1 is a small GTPase protein from the Rho family that regulates cell polarization and migration. It plays a critical role in many cellular processes, such as cell adhesion, spreading, and differentiation.
Question 2: How does Rac1 function?
Rac1 functions by cycling between an active GTP-bound state and an inactive GDP-bound state. When activated, Rac1 binds to and activates a number of downstream effectors, including PAKs, WAVE, and WASP, which regulate the actin cytoskeleton.
Question 3: What is the role of Rac1 in cell polarity?
Rac1 plays a crucial role in establishing and maintaining cell polarity. It regulates the formation of lamellipodia and filopodia, which are essential for cell movement and adhesion.
Question 4: What is the role of Rac1 in cell migration?
Rac1 is a key regulator of cell migration. It promotes cell movement by regulating the formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions.
Question 5: What are the implications of Rac1 dysregulation?
Dysregulation of Rac1 activity has been implicated in a number of diseases, including cancer and immune disorders.
Question 6: How can Rac1 activity be regulated?
Rac1 activity can be regulated by a number of factors, including guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), and guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors (GDIs).
This concludes our FAQ section about Rac1. For more information, please refer to the provided link to the full article on Rac1.
Tips
Rac1 is a small GTPase that plays a crucial role in cell polarity and migration. It is involved in various cellular processes, including cell adhesion, cell spreading, and chemotaxis.
Tip 1: Understanding Rac1 Activation
Rac1 activation is stimulated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), such as Tiam1 and Vav. These GEFs promote the exchange of GDP for GTP, leading to Rac1 activation. Activated Rac1 interacts with various effectors, including WAVE complex, PAK, and JNK, to regulate downstream signaling pathways.
Tip 2: Regulation of Cell Adhesion
Rac1 controls cell adhesion by regulating the formation and disassembly of focal adhesions. Activated Rac1 promotes the assembly of new focal adhesions at the leading edge of migrating cells, while it also triggers the disassembly of older focal adhesions at the trailing edge. This dynamic regulation of cell adhesion allows cells to polarize and move efficiently.
Tip 3: Induction of Cell Spreading
Rac1 is involved in the initial spreading of adherent cells on a substrate. Upon cell attachment, Rac1 is activated and induces the formation of lamellipodia, which are broad, sheet-like protrusions that drive cell spreading. Rac1 also regulates the assembly of actin stress fibers, which provide structural support to the cell.
Tip 4: Control of Chemotaxis
Rac1 plays a crucial role in chemotaxis, the directed migration of cells towards chemoattractant gradients. Rac1 is activated in response to chemoattractants and promotes the formation of a leading edge on the side of the cell facing the chemoattractant. This leads to directional cell migration.
Tip 5: Implications in Disease
Dysregulation of Rac1 activity has been linked to various diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative disorders. In cancer, aberrant Rac1 signaling can promote cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. In autoimmune disorders, dysregulated Rac1 activity can contribute to excessive inflammation and tissue damage.
Understanding the role of Rac1 in cell polarity and migration is critical for deciphering cellular processes and developing therapeutic strategies for diseases associated with Rac1 dysregulation.
Rac1: A Key Player In Cell Polarity And Migration
Rac1, a member of the Rho GTPase family, plays a pivotal role in regulating cell polarity and migration, orchestrating cellular processes essential for development, immunity, and tissue repair. Its diverse functions are mediated through multiple signaling pathways, affecting cytoskeletal dynamics, cell-cell adhesion, and gene expression.
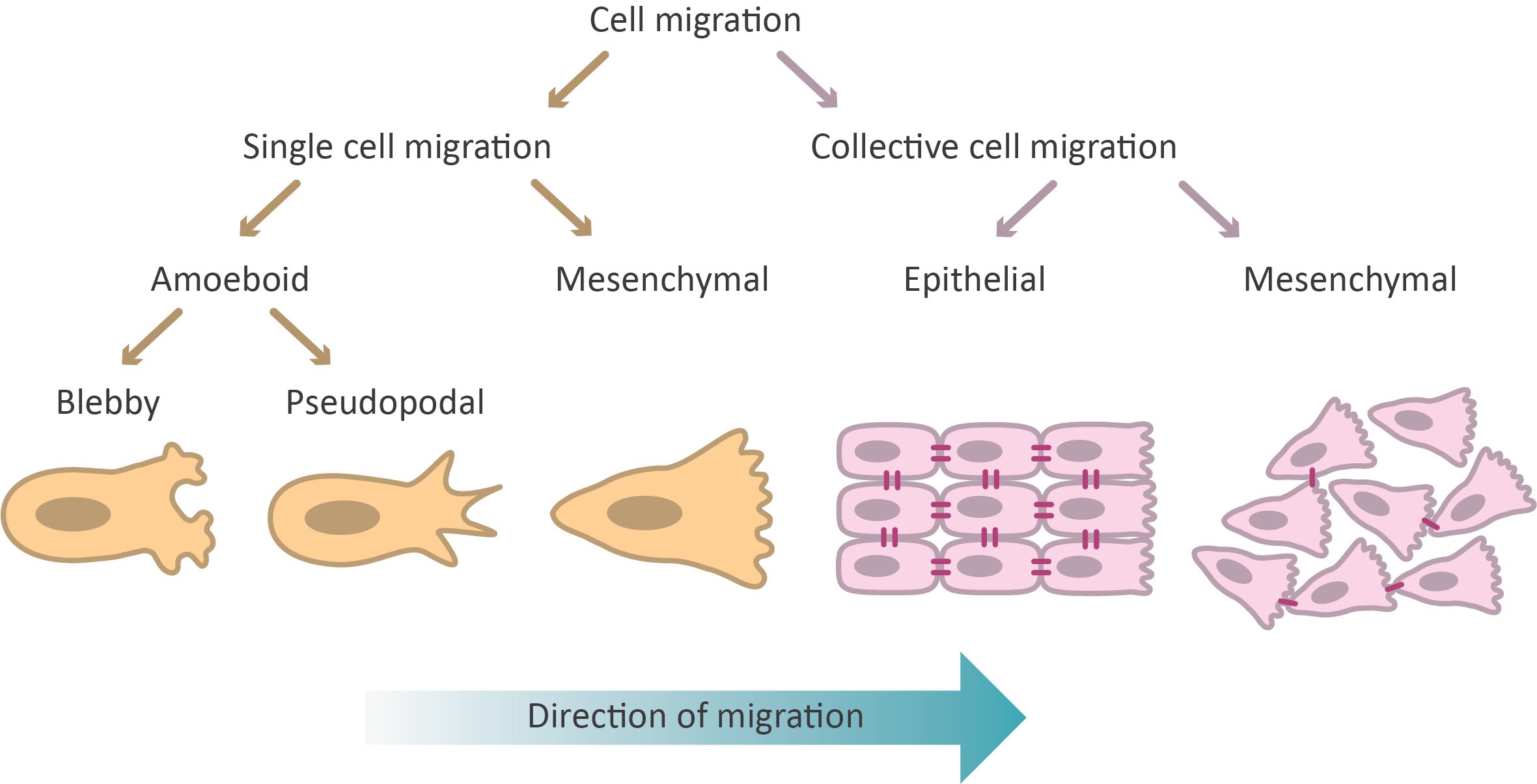
14 Astounding Facts About Cell Migration - Facts.net - Source facts.net
- GTPase Activity
- Cytoskeletal Remodeling
- Adhesion Regulation
- Morphogenesis Control
- Migration Initiation
- Immune Cell Function
Rac1's GTPase activity acts as a molecular switch, controlling its interactions with downstream effectors. By regulating cytoskeletal remodeling, Rac1 influences cell shape, polarity, and movement. It modulates cell-cell adhesion through integrin signaling, impacting cell-matrix interactions and collective cell behaviors. Rac1 also plays a crucial role in morphogenesis, orchestrating tissue and organ formation during development. Its involvement in migration initiation is essential for immune cell trafficking, wound healing, and cancer metastasis. Furthermore, Rac1 is implicated in immune cell function, regulating phagocytosis, antigen presentation, and T cell activation.
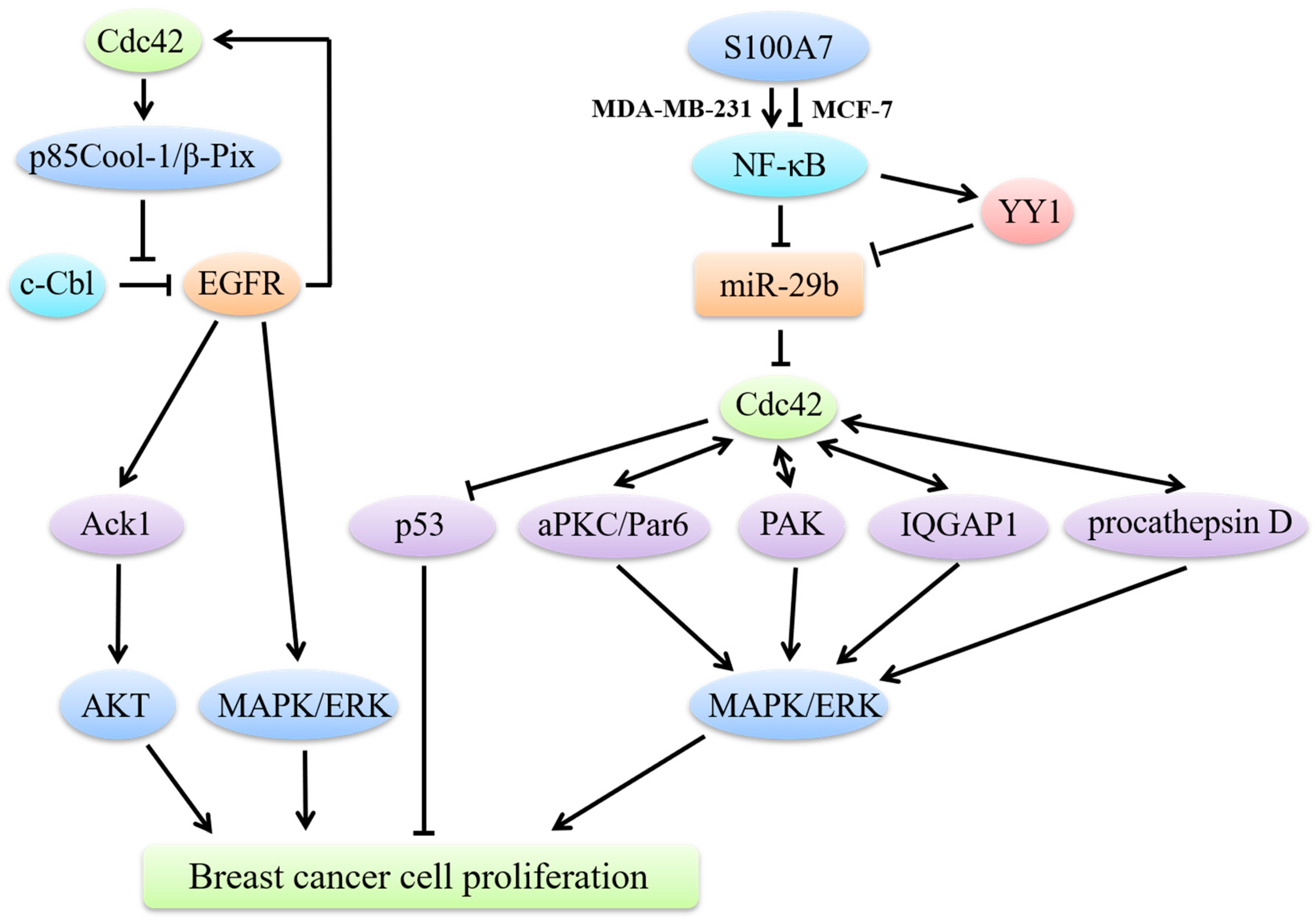
Cdc42 Signaling - Inhibition of Rac1 or Cdc42 signaling in adherent - Source harrykanee.blogspot.com
Rac1: A Key Player In Cell Polarity And Migration
Rac1, a small GTPase, plays a pivotal role in orchestrating cell polarity and migration, processes that are vital for cellular function. It acts as a molecular switch, toggling between inactive GDP-bound and active GTP-bound states to regulate downstream effectors involved in cytoskeletal dynamics.
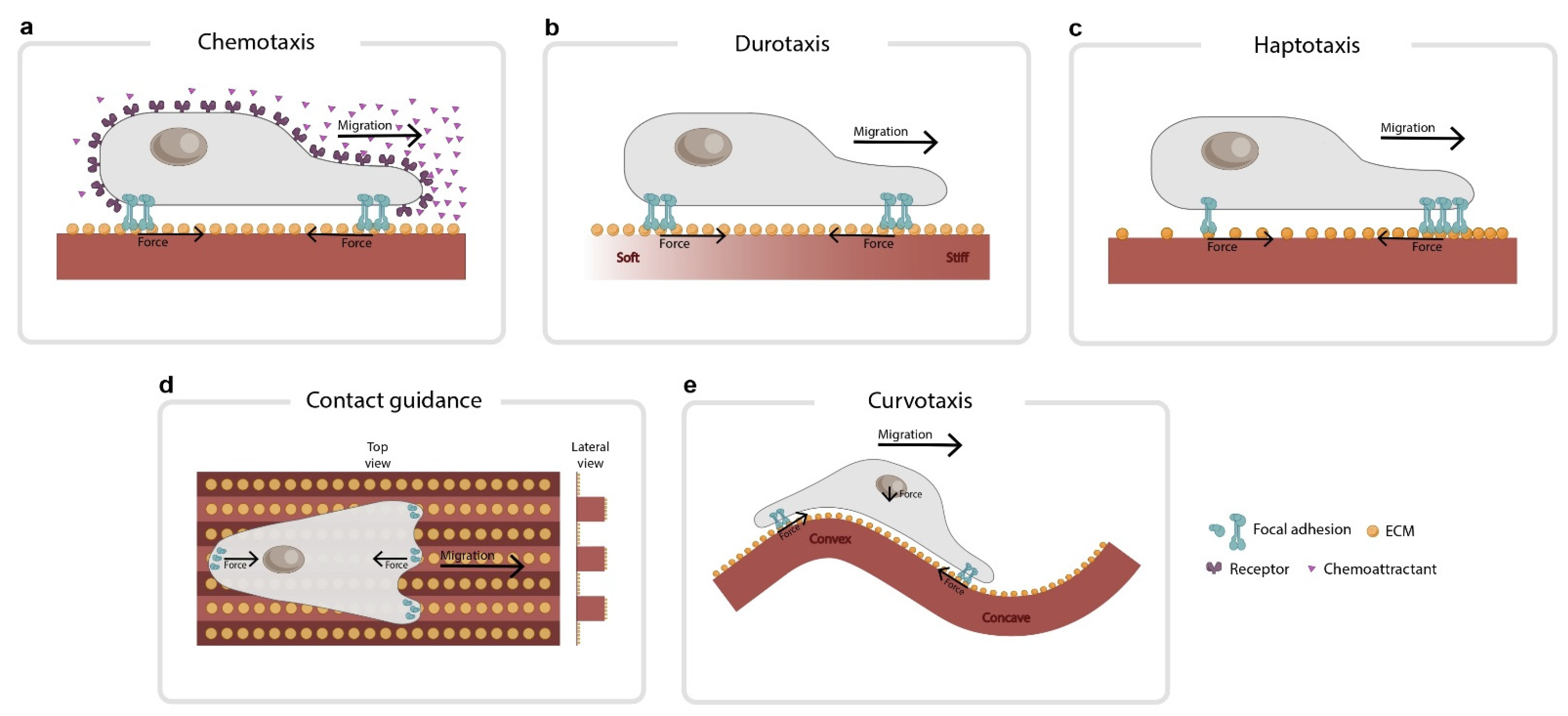
Biophysica | Free Full-Text | The Forces behind Directed Cell Migration - Source www.mdpi.com
Cell polarity is established through the asymmetric distribution of proteins and organelles. Rac1 contributes to this process by promoting the formation of lamellipodia, protrusive structures at the leading edge of the cell, and inhibiting the formation of filopodia. By controlling the localization and activity of its effectors, Rac1 helps determine the direction of cell migration.
This understanding of Rac1's role in cell polarity and migration has practical significance in various fields of biology and medicine. For instance, in cancer biology, manipulating Rac1 activity has been explored as a potential therapeutic strategy to inhibit tumor cell metastasis.
Conclusion
Rac1's role in cell polarity and migration is a key aspect of its broader function in regulating cellular processes. By understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying Rac1's activity, researchers can gain insights into the fundamental principles of cell biology and develop potential therapeutic interventions for various diseases.
Further research is needed to fully elucidate the complexities of Rac1 signaling and its interactions with other cellular components. This will deepen our understanding of how cells function and respond to their environment, opening up new avenues for scientific exploration and medical advancements.